2026 Leading Debug Agent Skill In-Depth Comparison: The Ultimate AI Debugging Skills Selection Guide
As AI-assisted programming becomes increasingly prevalent, developers have grown accustomed to letting LLMs write code, but the debugging phase often falls short due to AI "hallucinations." AI tends to get trapped in "guessing mode," constantly modifying code to verify hypotheses, which not only consumes massive amounts of tokens but also pollutes the codebase.
In our previous article Debug Agent Skills Guide: From "Guessing Code" to Runtime Reality, we deeply analyzed the fundamental cause of this phenomenon—the chasm between "static text" and "dynamic runtime"—and argued why Debug Agent Skills are the key to breaking this deadlock.
The Core Problems Debug Agent Skills Solve:
- Eliminate the "guess-check" loop in AI debugging
- Provide authentic runtime context
- Enhance bug fix accuracy
- Reduce debugging time and token consumption
- Enable automated debugging workflows
Having understood "why use AI debugging tools," we now turn to solving "which one to use."
I. In-Depth Comparison of 5 Leading Debug Agent Skills: Find the AI Debugging Solution That's Right for You
Faced with the proliferation of AI debugging tools on the market, how should developers choose? This article will conduct an in-depth horizontal evaluation of the 5 mainstream Debug Agent Skill products based on industry benchmarks.
1. Systematic-debugging
Product Positioning: Methodology-driven debugging tool for complex systems
Core Logic: Iterative verification based on log probes (TDD-style), which is a "modify-run-verify" loop process.
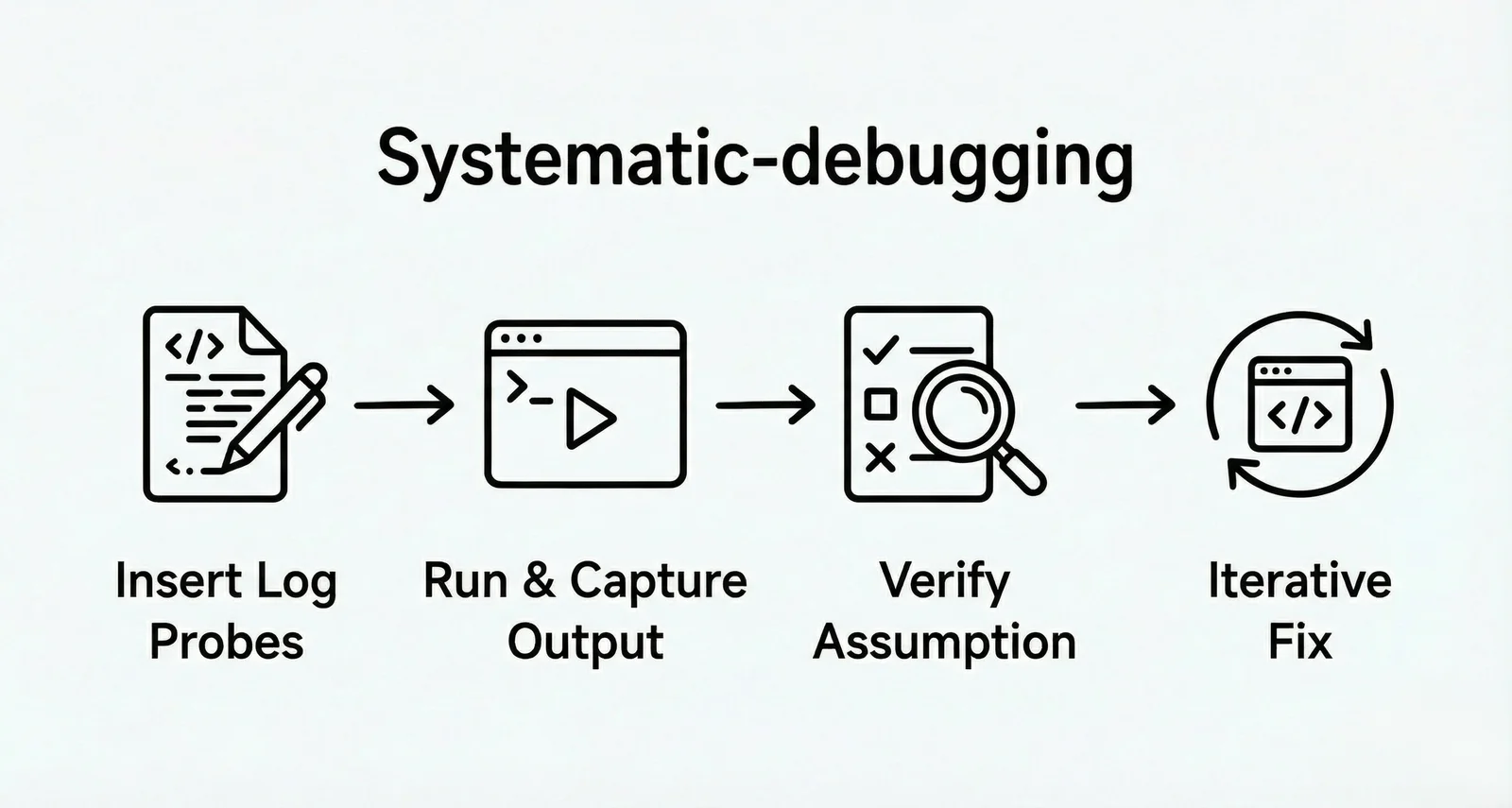
Debug Workflow:
-
Agent analyzes code logic and directly modifies source code by inserting log probes like
console.log -
Triggers code execution and captures actual output
-
Compares output with expectations (similar to Test-Driven Development)
-
Corrects code based on discrepancies until verification passes
-
Applicable Scenarios: Complex production environment bug debugging, team collaboration debugging requiring systematic methodology, development scenarios with deep TDD workflow integration, and processes requiring repeatable and verifiable debugging.
-
Core Advantages:
- Systematic methodology, avoiding inefficient "guess-check" style debugging
- Enforced execution, mandating completion of each phase before advancing, ensuring debugging quality
- Complete software development workflow
- Automatic triggering mechanism, no manual invocation needed
- Seamless integration with agent-driven development
-
Usage Limitations:
- Heavy process, small bugs may be over-engineered
- Strict rule adherence may reduce flexibility
- Steep learning curve, requiring understanding of the entire Superpowers ecosystem
- Primarily targets Claude Code; other platforms require manual configuration
2. Debug (Inbox Zero)
Product Positioning: Log-intelligent solution for long-term project maintenance
Core Logic: Structured closed-loop of log streams (Log-to-JSON), which is a process of converting unstructured information into machine-readable data.
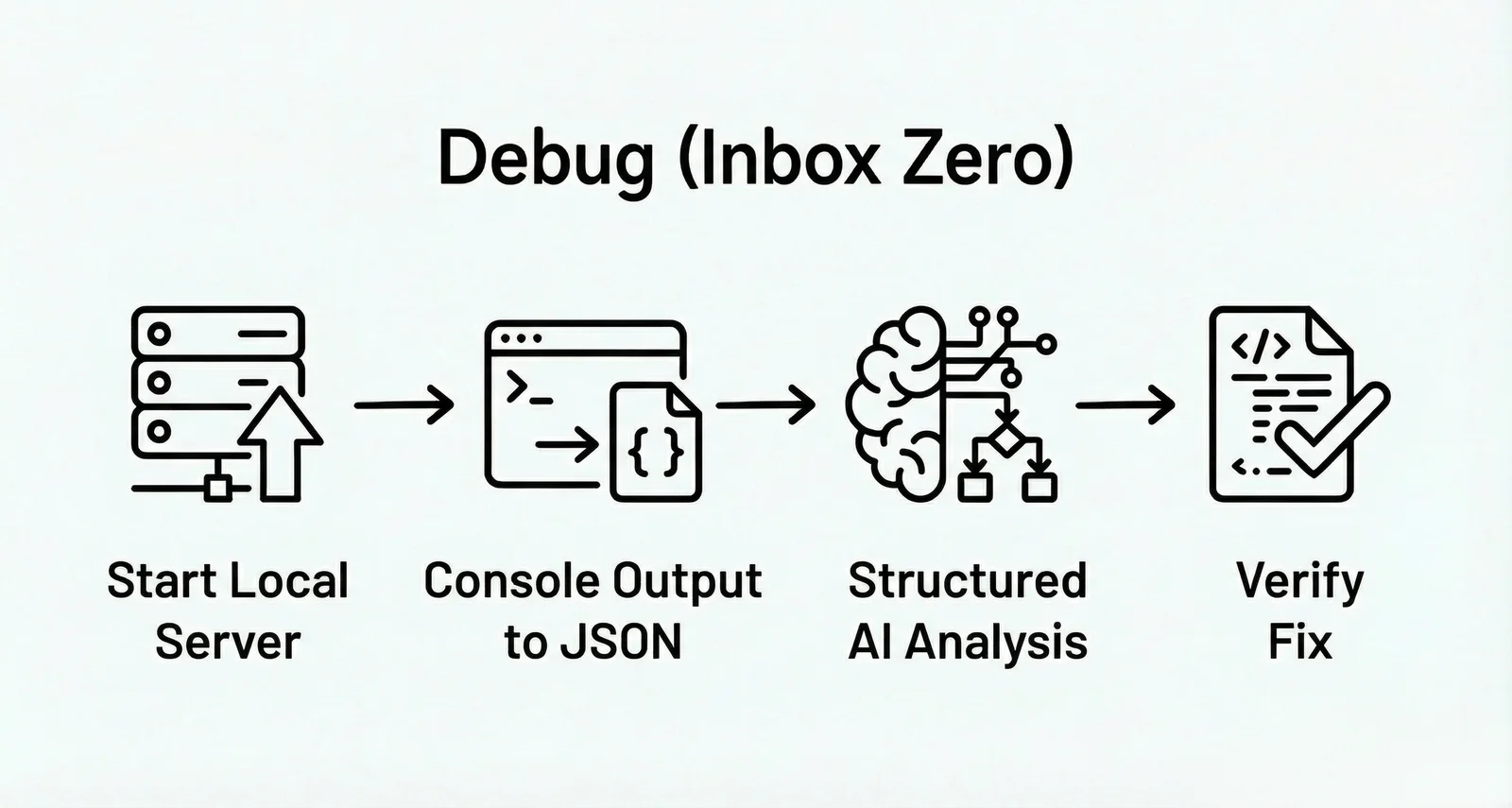
Debug Workflow:
-
Start a local log server
-
When the program runs, the server intercepts console output and converts it in real-time to structured JSON data
-
Agent subsequently queries this structured data, analyzes based on concrete log records, and generates fix solutions
-
Achieves closed-loop verification
-
Applicable Scenarios: Long-term maintenance of large projects, team collaborative development requiring consistency in code style and architectural decisions, scenarios with frequent regression test failures.
-
Core Advantages:
- Prevents degradation, avoiding repeating the same mistakes through historical records
- Automated log capture and analysis, reducing manual work and iteration time
- Architectural protection, avoiding "breaking architecture to fix bugs"
-
Usage Limitations:
- Depends on correct instrumentation, incomplete logs may lead to uncertain results
- Setup overhead for simple problems (starting server, instrumentation)
3. Debugging-strategies
Product Positioning: Multi-agent orchestration solution for full-stack scenarios
Core Logic: Knowledge retrieval-assisted manual troubleshooting (RAG + Checklists), which is a "retrieve-guide-execute" assistance process.
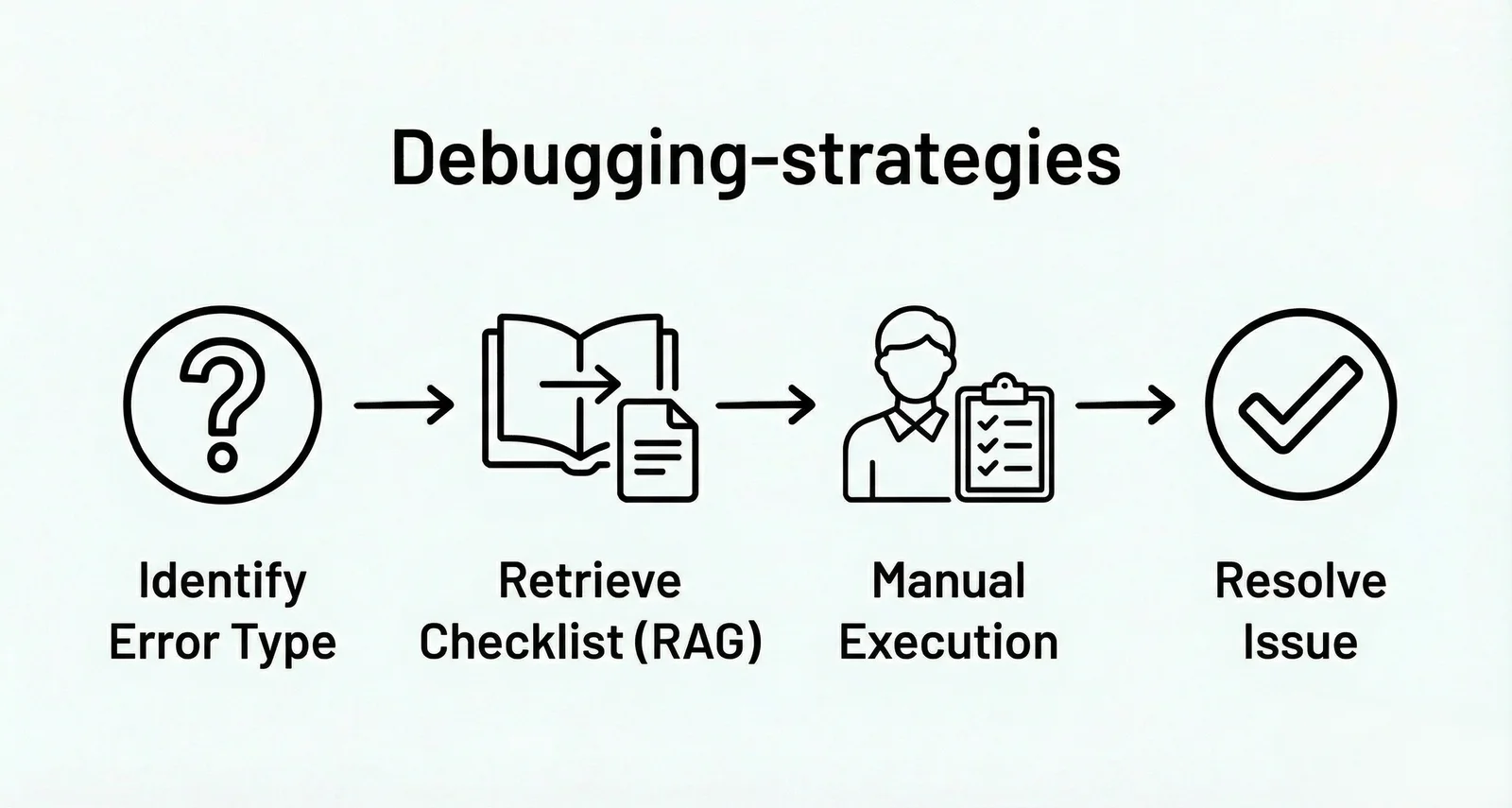
Debug Workflow:
-
Agent doesn't directly run or modify code, but identifies error types (e.g., 404, NPE)
-
Calls corresponding troubleshooting checklists (Cheatsheets) from an internal knowledge base via RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
-
Agent outputs specific troubleshooting strategy steps to the developer
-
Developer manually executes checks to identify the problem
-
Applicable Scenarios: Large-scale team collaborative development, projects requiring multi-language support (Python, Rust, JS/TS, etc.), complete DevOps/SRE workflows, full-stack scenarios from development to deployment.
-
Core Advantages:
- Extremely comprehensive skill library
- Granular plugin architecture, load on demand, optimizing token usage
- Multi-model orchestration (Opus/Sonnet/Haiku), balancing cost and capability
- Complete isolation of each plugin, easy to manage
-
Usage Limitations:
- Large scale, beginners may not know where to start
- Requires understanding multi-agent collaboration patterns
- Documentation scattered across multiple markdown files
- High migration costs dependent on Claude Code ecosystem
4. Debug-mode
Product Positioning: Open-source debugging instruction set (Prompt Engineering best practices)
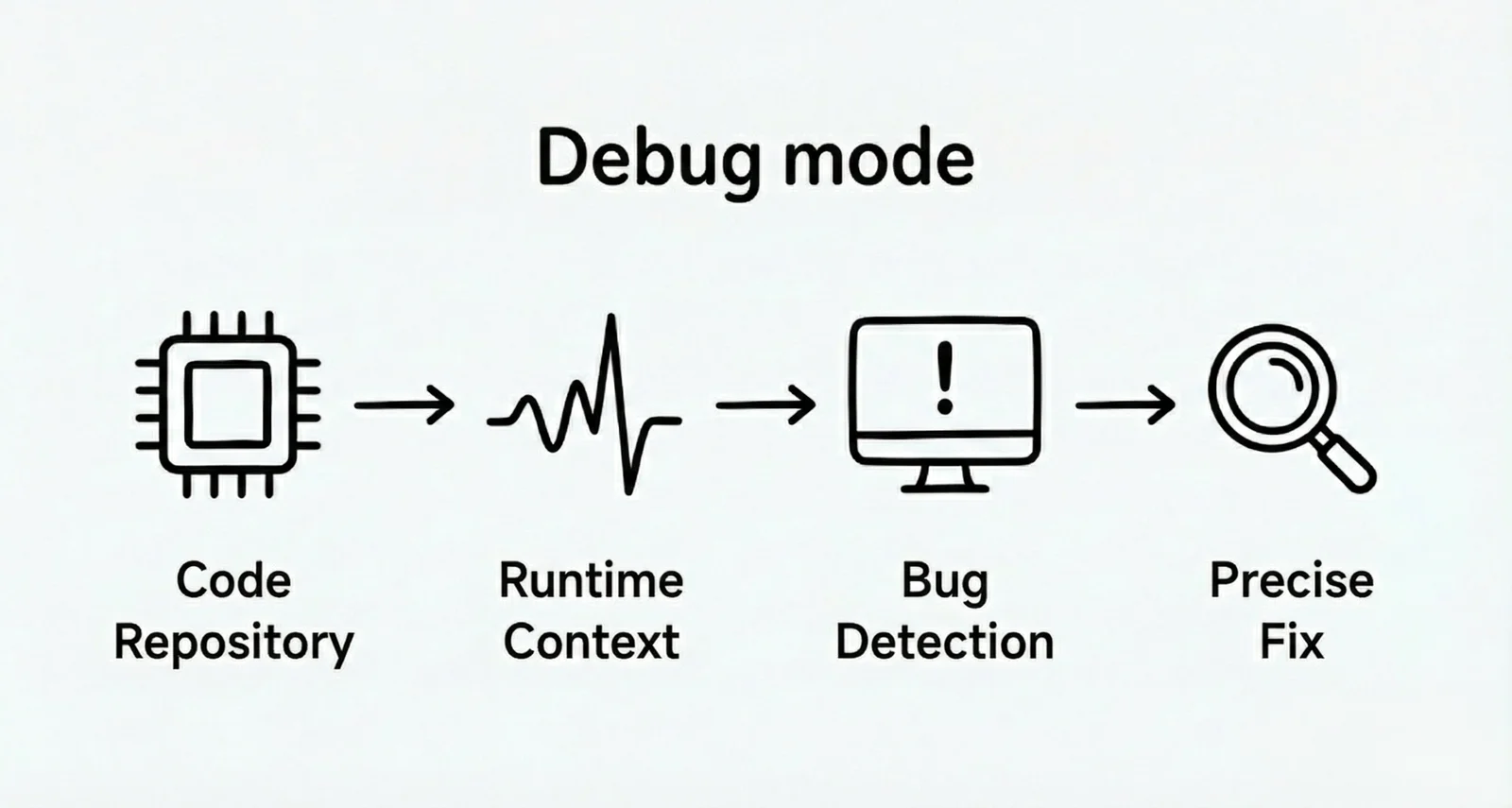
Core Logic: Root cause first constrained reasoning (Prompt-Enforced), which is a process of strictly constraining behavior through prompts.
Debug Workflow:
-
Through specific Prompt Engineering, the system forces the Agent to follow the "find root cause first, then write code" sequence
-
Agent must first propose hypotheses about bug causes and perform logical deduction
-
Only generate minimal viable changes (Minimal Changes) for verification, preventing AI from randomly spreading code modifications during debugging
-
Applicable Scenarios: Complex bugs requiring runtime logs, cross-language/cross-tech-stack debugging scenarios, gray-area problems requiring manual verification.
-
Core Advantages:
- Standardized AI reasoning path
- Human-machine collaboration design, combining AI efficiency with human judgment
- Automatic cleanup of instrumentation, keeping code clean
- Multiple hypothesis parallel testing, improving hit rate
-
Usage Limitations:
- Requires developers to have good prompt awareness
- Debugging speed is relatively slower (requires multiple reproductions)
5. Syncause Agent Skill
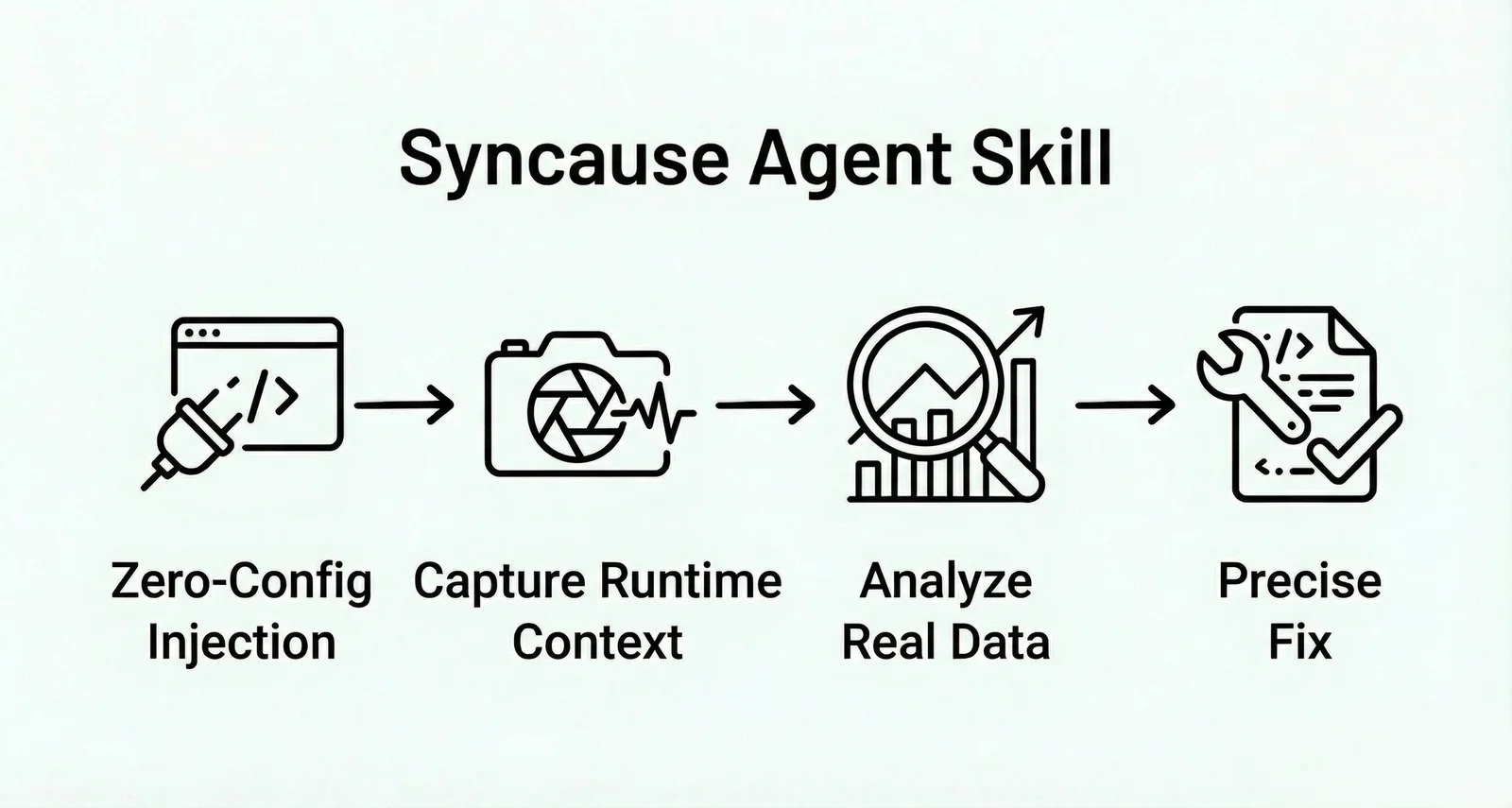
Product Positioning: Zero-configuration runtime context injection tool for local development
Core Logic: Direct injection of runtime context (Runtime Context Injection), which is a "fully automated on-site forensics" process.
Debug Workflow:
-
Without requiring manual server configuration or instrumentation, Agent automatically injects runtime context collection tools
-
When the program runs, the tool directly captures real execution traces and variable states (Runtime Facts)
-
Agent bypasses logical inference and directly locks down the bug location based on these authentic on-site data and fixes it
-
Applicable Scenarios: Debugging logic errors encountered during local development, local reproduction and analysis of complex bugs, rapid understanding of runtime state when taking over legacy code, deep diagnostics when unit tests fail.
-
Core Advantages:
- Zero configuration: No need to set up servers or complex instrumentation, ready to use out of the box
- Root cause lockdown: Eliminates AI hallucinations through real variable values, rejecting "trial-and-error" fixes
- Data privacy and security: Focused on local environments, avoiding risks of sensitive production data leakage
- Lightning-fast feedback: Shortens the "guess-verify" loop to simple "observe-fix"
-
Usage Limitations:
- Environment dependency: Requires actual code execution in local or sandbox environments
- Requires integration with a complete observability stack
II. How to Choose the Right AI Debugging Tool? Decision Matrix
| Your Need | Recommended Solution | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Need standardized debugging flow | Systematic-debugging | Enforces methodology |
| Long-term project maintenance | Debug (Inbox Zero) | Historical record protection |
| Large-scale team full-stack dev | Debugging-strategies | Complete skill library |
| IDE native / AI workflow config | Debug-mode | Low-cost, hypothesis-driven fixes |
| Cover simple to very complex issues | Syncause Agent Skill | Zero-config runtime debugging |
III. Conclusion and Recommendations
The chasm between "static text" and "dynamic runtime" is the main reason AI struggles with complex debugging. Debug Agent Skills provide the missing link, upgrading debugging from "spell-checking" to "logical reasoning" through runtime context injection and enforcing scientific debugging processes, thereby solving problems beyond context limitations and greatly improving debugging efficiency.
This article compared five mainstream projects: Systematic-debugging, Debug, Debugging-strategies, Debug-mode, and Syncause Agent Skill. Each solution has its focus, from automated runtime fact injection to methodology guidance, jointly advancing AI Agent debugging. Choosing the right Debug Agent Skill should comprehensively consider your project's specific needs, team's tech stack, data privacy requirements, budget, and other factors. In practical development, you can even combine multiple tools and methods to build the Agent debugging workflow that best suits your scenario.
If you're tired of AI's "trial-and-error fixes" and the fatigue of repeated rework, and yearn for AI Agents to truly have a "bird's-eye view" to solve complex problems, then consider integrating Syncause Debug Skill. Syncause is committed to making runtime facts the foundation of AI reasoning through runtime context injection, thereby achieving zero-configuration automated debugging, fundamentally eliminating hallucinations, and having zero impact on production environments. Setup can be completed in just 2 minutes, letting your AI Agent make fewer guesses, fewer reworks, and ensuring every fix is precise and controllable.